4. Working With a Single Table: Superstore Dataset
Working With a Single Table: Superstore Dataset

Our first dataset, that consists of a single table, is called Superstore. Superstore is one of the most popular datasets for educational purposes. You can learn more about this dataset on the Kaggle page.
Exploring Tabs:
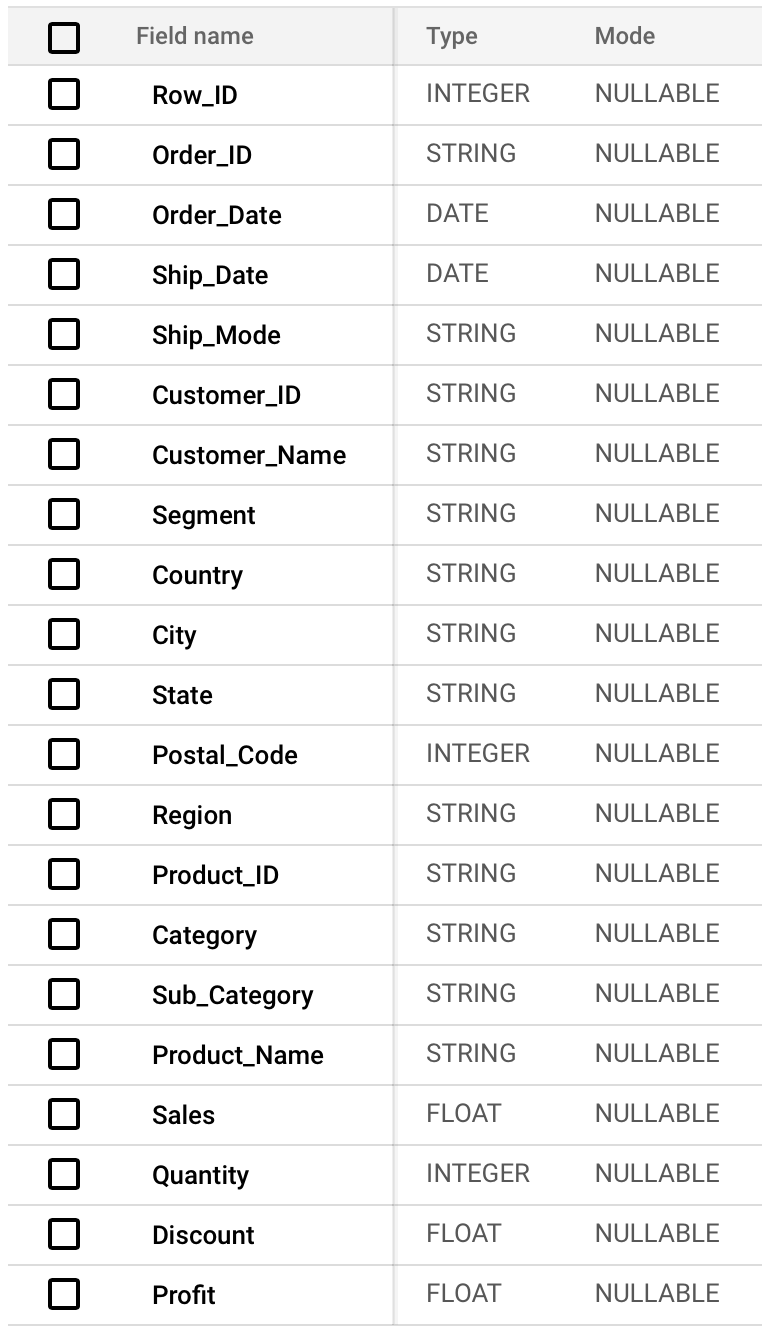
Let’s first start by exploring different types of columns in our table. Our table consists of 21 columns of different types.
Exploring the Schema:
Overall, there are many column types in Google BigQuery:
- String: Stores alphanumeric characters, symbols, and spaces. It's used for text data.
- Bytes: Used for storing binary data.
- Integer: Stores whole numbers, both positive and negative.
- Float: A floating-point number used for storing decimals.
- Boolean: Stores TRUE or FALSE values.
- Timestamp: For dates and times, including both a date and a time portion, with timezone information.
- Date: Stores only the date, with no time portion.
- Time: Stores only the time of day, with no date.
- DateTime: Combines both date and time but without timezone information (unlike Timestamp).
- Numeric: For storing high-precision decimal numbers. It's a fixed-point type with specific precision and scale.
- Bignumeric: An extension of the Numeric type that allows for even larger and more precise numbers, with greater scale and precision.
- Geography: Used for storing geographical data, like points, lines, and polygons on the Earth's surface. This type is specifically designed for spatial data and supports various spatial functions.
- Array: A collection of elements of the same type.
- Struct: A complex data type that can contain multiple fields with different data types, similar to a row in a table, allowing for nested and hierarchical data.
In our table, we have only four column types – Integer, String, Float, and Date. However, some columns have an incorrect column type (Postal_Code).
Understanding the Modes
"Mode" in BigQuery refers to an attribute of a table field (column) that specifies how the field values are arranged. It determines whether a column can accept multiple values per row, a single value, or if it can be empty. The modes in BigQuery are:
- NULLABLE: This is the default mode. It means that the field can contain zero or one value per row. In other words, the field can either have a value or be NULL.
- REQUIRED: Fields set to this mode must have a value in every row. NULL values are not allowed in REQUIRED fields.
- REPEATED: This mode allows the field to contain an array of values in a single row. Essentially, a REPEATED field can have zero, one, or multiple values in a single row. This is useful for representing multi-valued properties, such as multiple tags associated with a blog post in a "tags" field.
These modes are crucial for defining the schema of a table in BigQuery, allowing for flexibility in data modeling and ensuring data integrity according to the defined schema rules.